AWS Lamda:
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It provides an event-driven computing service, allowing developers to focus on writing code without worrying about infrastructure management. Some key benefits of AWS Lambda include:
Auto-scaling: AWS Lambda automatically scales your functions in response to incoming request volume, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Pay-per-use pricing: With Lambda, you only pay for the compute time consumed by your functions, making it cost-effective for applications with varying workloads.
Integration with other AWS services: Lambda seamlessly integrates with other AWS services, such as API Gateway, S3, DynamoDB, and more, enabling powerful serverless architectures.
High availability and fault tolerance: AWS Lambda manages the underlying infrastructure, ensuring your functions are highly available and fault-tolerant
Let’s Get Started
1. Setup Spring Boot
To create Spring Boot project, you can use InteliJ or Spring Initializr
1.1. Project Structure and Dependencies
In this project, we going to use Spring Boot version 2.7.6, Spring Cloud version2021.0.5 and Java 11. We need a couple of dependencies for development.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-function-adapter-aws</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-lambda-java-events</artifactId>
<version>3.11.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-lambda-java-core</artifactId>
<version>1.2.2</version>
</dependency>
We need a couple more spring cloud dependencies management
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
In the final step, we need to build our application shade since some dependencies are not required to run on AWS Lambda.
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.4</version>
<configuration>
<createDependencyReducedPom>false</createDependencyReducedPom>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<artifactSet>
<excludes>
<exclude>org.apache.tomcat.embed:*</exclude>
</excludes>
</artifactSet>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
Our project configuration is ready to serve requests, next we need to create a Java class for handling requests. In my case, I require a lambda response back as json so, the handle request method needs to be APIGatewayV2HTTPResponse
public class RequestServiceHandler implements RequestHandler<Map<String, Object>, APIGatewayV2HTTPResponse> {
@Override
public APIGatewayV2HTTPResponse handleRequest(Map<String, Object> stringObjectMap, Context context) {
System.out.println("Lambda function invoke by Java");
return APIGatewayV2HTTPResponse.builder()
.withStatusCode(200)
.withHeaders(Map.of("Content-Type", "application/json"))
.withBody("{\"message\": \"success\"}")
.build();
}
}
Our application is ready to build and deploy into Lambda AWS. Build application by using mvn clean package
1.2. Working with DynamoDB
In the development environment, we need to add DynamoDB SDK into our project.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-java-sdk-sns</artifactId>
<version>1.12.367</version>
</dependency>
Inside handler class, we need to initial AmazonDynamoDBClientBuilder
AmazonDynamoDB amazonDynamoDB = AmazonDynamoDBClientBuilder.standard().withRegion(Regions.US_EAST_1).build();
To save data into DynamoDB we need to construct a Map with a key as Stringand value as AttributeValue
Map<String, AttributeValue> map= new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", new AttributeValue(UUID.randomUUID().toString()));
amazonDynamoDB.putItem("your_table_name", map);
1.3. Working with SNS
Similarly, to DynamoDB we also need an SNS SDK
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-java-sdk-sns</artifactId>
<version>1.12.367</version>
</dependency>
Back to handler class, we need to initial AmazonSNS
AmazonSNS amazonSNS = AmazonSNSClientBuilder.standard().build();
Publish your message SNS Topic by using Topic ARN
amazonSNS.publish("your_topic_arn", "Hello from Lambda!");
2. Deploy Spring Boot to AWS Lambda
Deploy your application to AWS Lambda we need to create an S3 Bucket to store our jar file
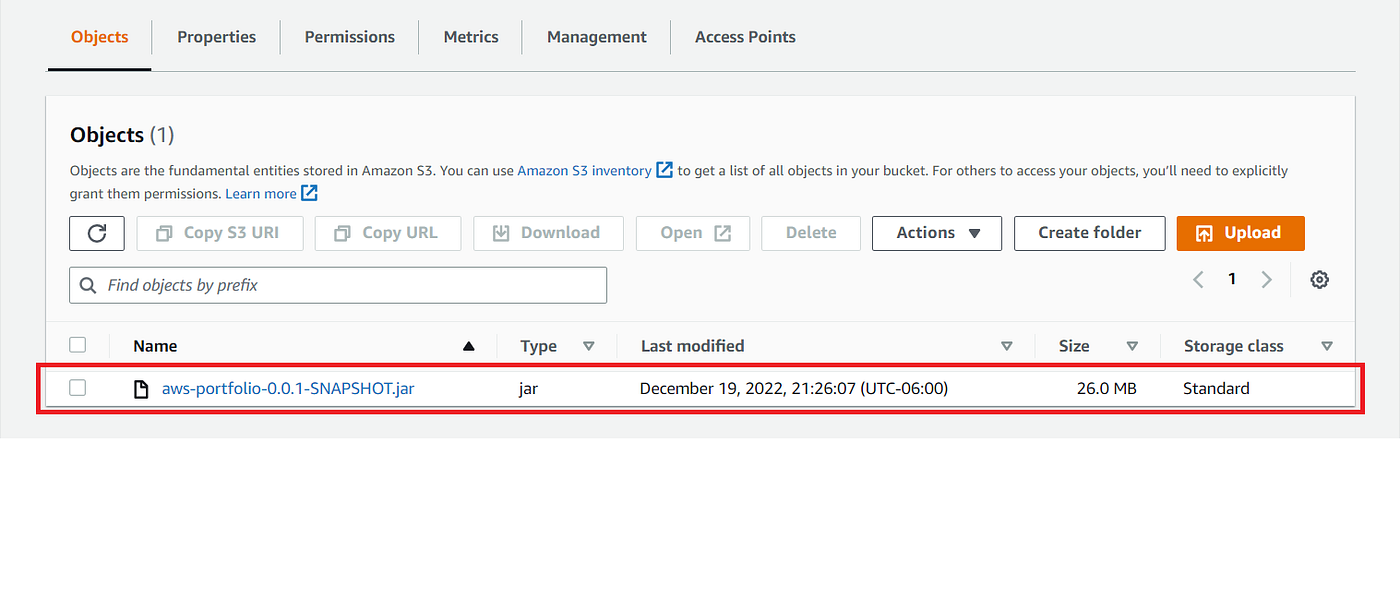
Deploy application from S3 Bucket
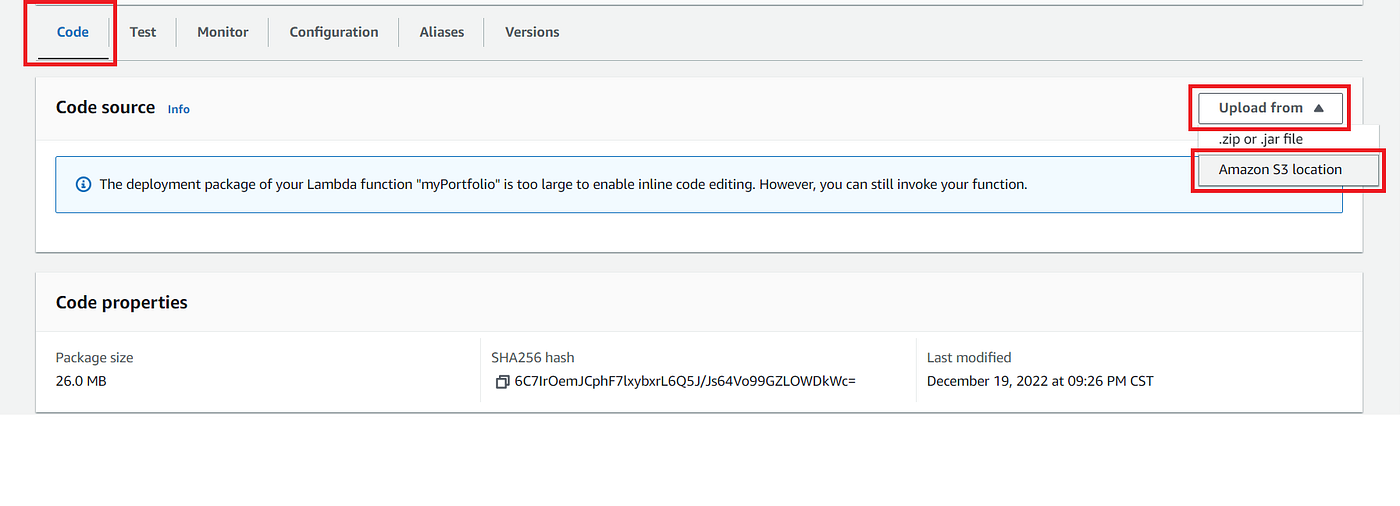
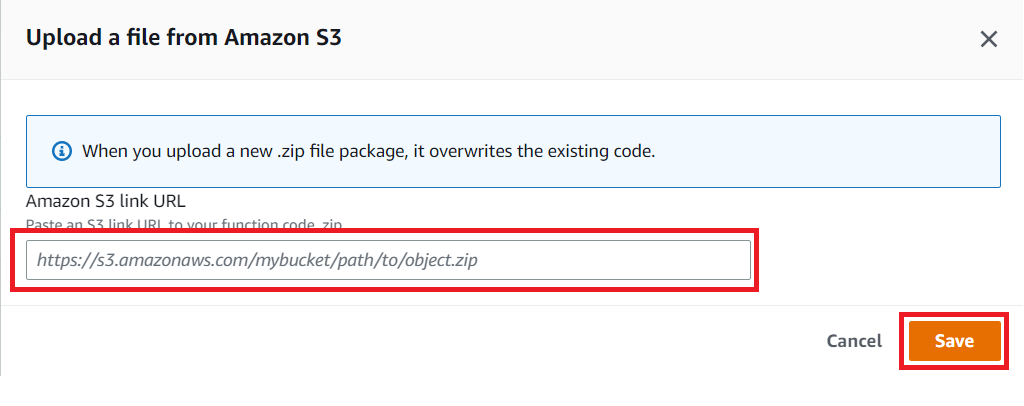
Enter bucket endpoint
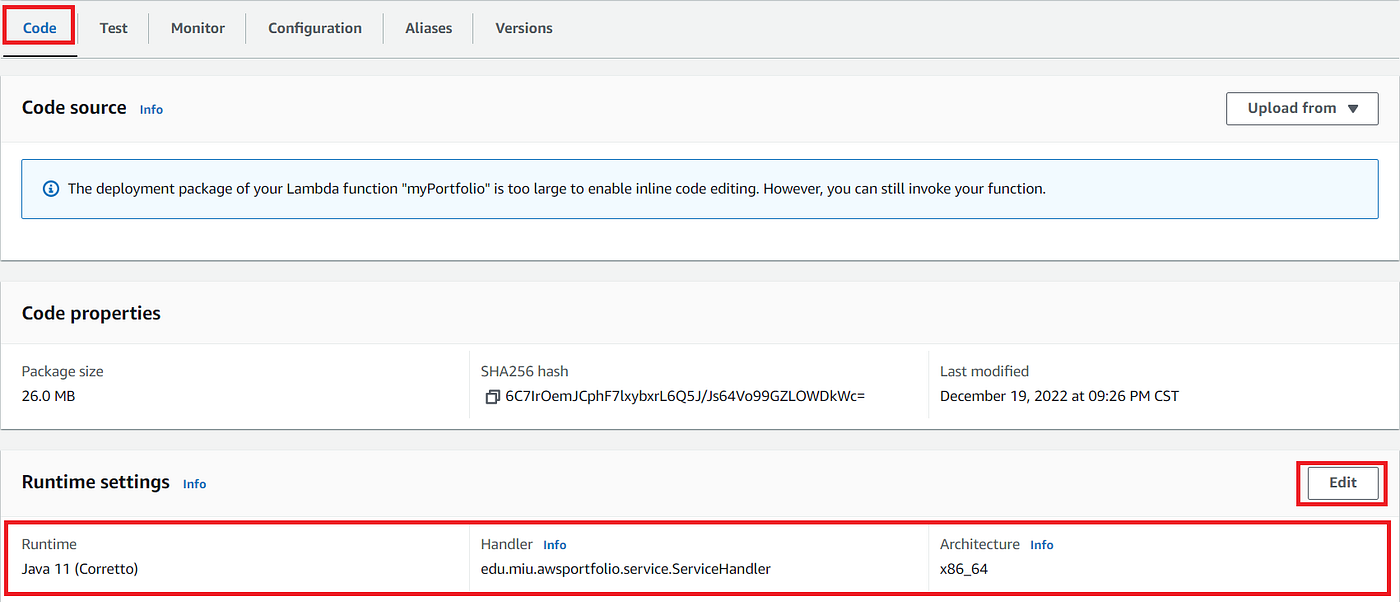
Config your handler class in Runtime Settings
Conclusion
The combination of Spring Cloud Function and AWS Lambda offers a powerful and streamlined approach to building serverless applications. With the recent support for Java 17 in AWS Lambda, developers can now take advantage of the latest language features and enhancements. By adopting this serverless architecture, you can focus on writing business logic while leveraging the scalability and cost benefits of AWS Lambda. So, go ahead, explore the possibilities, and unleash the true potential of serverless computing with Spring Cloud Function and AWS Lambda's Java 17 support.
Remember to keep up with the latest updates from both Spring Cloud Function and AWS Lambda to stay informed about new features and improvements. Happy serverless coding!

